If there is a single buzzword that’s taken up ubiquitous residence in the most fashionable quarter of ETFtown these past few years, it’s “Ex-Financials” – index products designed to give you exposure to a given geography or market but with the financial stocks left out. The reasons are obvious, nobody wants to have exposure to banks when they know the books are being cooked with complicit government regulators looking on. And lest you think the suspension of GAAP standards is merely a US phenomenon, you should see the kind of shit European banks are getting away with.
And Chinese banks? Forgetaboutit.
Which brings me to a new piece of research from Jeremy Schwartz of WisdomTree. Schwartz’s shop has an ex-financials China Dividend ETF (could that be any buzzier?) and he explains that Chinese indices are still way too heavy with financials and bank stocks to be attractive in and of themselves (unless you’re bullish on Chinese real estate development loans, lol). Financials make up a whopping 50% of some mainstream China indices, for example. So WisdomTree created $CHXF as a way to get exposure to everything else and have a dividend orientation. We’re not using the fund here, we’re a little more old-fashioned with our EM exposure at the moment.
But the more interesting question raised here is “If I don’t like the banks of a country, why would I want to be in their stock market at all.” Schwartz’s answer to that below is a good one, the US stock market is a perfect example of why:
If financials are likely to be weak, why bother investing in a given market? An initial reaction to any “ex-financials” equity approach might be to think that if the financial sector is weak, then the rest of the market is likely to also be weak.
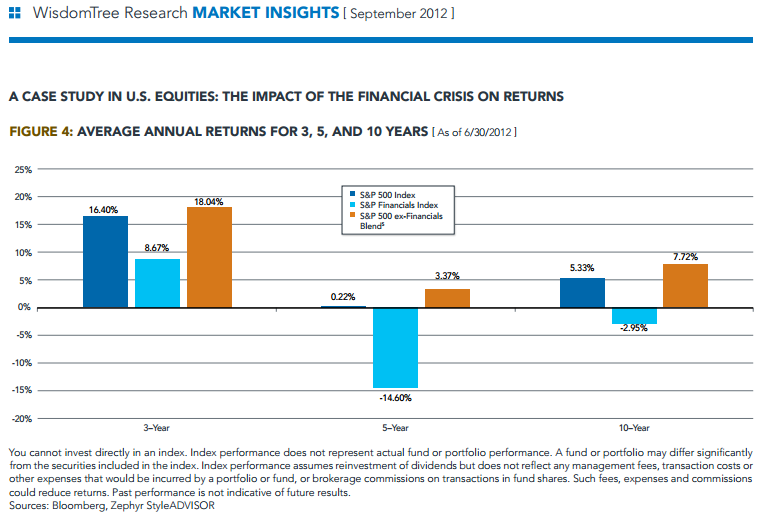
In that regard, the United States, through the use of the S&P 500 Index, presents an interesting case study over the past decade. We look to this index and country mainly because of the breadth of history available—the financial crisis of 2008–09 was without question the worst since the Great Depression of the 1930s. China’s equity markets do not have such a record of performance history from which to draw. Figure 4 indicates that over the past decade, in the face of such a severe crisis, there has been a decoupling between the performance of the broader S&P 500 Index and that of the S&P 500 Financials Sector Index. While we can’t say that this will always be the case or that similar results would necessarily hold true for China’s equities, we can say that it is possible for the performance of financials can to be markedly different from that of other sectors.
- most noteworthy is the average annual performance over the five years ended June 30, 2012, where even though the financials component was down by over 14% per year, the broader S&p 500 index was pulled up enough by the other nine sectors to generate a positive return. the other nine sectors, in an equal-weighted blend, had over 3.3% average annual returns.
- on a 10-year basis, while the financial sector was down nearly 3% per year, the other nine sectors averaged nearly 7.75% per year.
Josh here – by ignoring US banks but keeping your exposure to the rest of the productive economy, you saw quite a difference in performance even despite a rocky ride for the indices overall. Will the same be said years from now about those who kept China on and zeroed out their Chinese bank exposure?




… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 54070 additional Info to that Topic: thereformedbroker.com/2012/09/19/ex-financials/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 7394 more Information on that Topic: thereformedbroker.com/2012/09/19/ex-financials/ […]